18 parts of the heart: names and functions
The human heart is a powerful biological pump responsible for maintaining blood flow throughout the body. Understanding the heart parts name and their functions is essential to grasp how the heart keeps us alive. In this article, we explain the 18 main parts of the heart, including how many muscles are in the heart and their specific roles.
Overview of the Human Heart
The heart is a muscular organ located slightly to the left behind the sternum, protected by the ribs. It connects to the lungs through a complex network of arteries and veins, allowing blood to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Its left side is stronger than the right because it pumps blood to the entire body, whereas the right side only pumps blood to the lungs.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Behind the sternum, slightly left |
| Structure | Muscular, asymmetrical |
| Function | Pumps blood; maintains circulation |
| Protection | Ribs, pericardium, connective tissue |
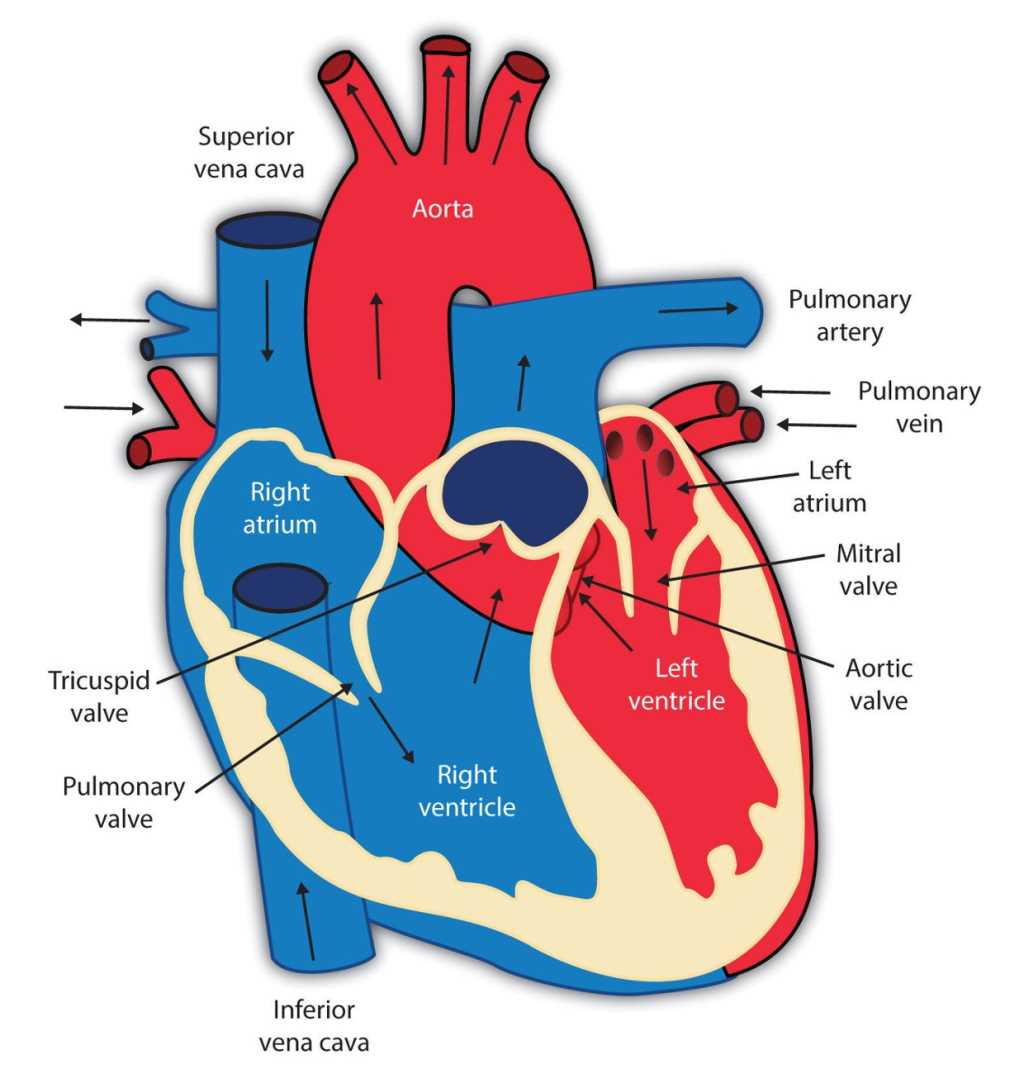
18 Parts of the Heart and Their Functions
1. Myocardium
- Contractile muscle layer responsible for pumping blood.
- Functions involuntarily; contraction signals originate within the heart.
- Thicker in ventricles and stronger on the left side.
(Answering “how many muscles are in the heart”: the myocardium is the main muscular tissue of the heart.)
2. Endocardium
- Smooth lining of the heart chambers.
- Composed of endothelial cells and connective tissue.
3. Pericardium
- Protective fibrous sac surrounding the heart.
- Consists of serous and fibrous layers.
- Allows free heart movement without friction.
4. Right Atrium (Right Auricle)
- Receives oxygen-poor blood from the superior and inferior vena cava.
- Sends blood to the right ventricle.
5. Right Ventricle
- Pumps blood to the pulmonary artery for oxygenation in the lungs.
- Contracts slightly before the left ventricle.
6. Tricuspid Valve
- Between right atrium and right ventricle.
- Prevents blood backflow using three connective tissue leaflets.
7. Pulmonary Valve
- Connects right ventricle to pulmonary artery.
- Opens during contraction to allow blood flow to lungs.
8. Left Atrium (Left Auricle)
- Receives oxygen-rich blood from four pulmonary veins.
- Sends blood to left ventricle through the mitral valve.
9. Left Ventricle
- Strongest heart chamber; pumps blood into the aorta.
- Generates higher blood pressure than the right ventricle.
10. Mitral Valve
- Separates left atrium and left ventricle.
- Prevents backflow during contraction.
11. Aortic Valve
- Controls blood flow from left ventricle to aorta.
- Designed to withstand high pressure.
12. Tendon Cords (Chordae Tendineae)
- Connect valves to papillary muscles.
- Prevent valve inversion during contraction.
13. Papillary Muscles
- Cone-shaped muscles inside ventricles.
- Keep atrioventricular valves closed to prevent blood reflux.
14. Sinoatrial (SA) Node
- Natural pacemaker of the heart.
- Initiates electrical impulses for contraction.
15. Atrioventricular (AV) Node
- Backup pacemaker.
- Transmits impulses from atria to ventricles if SA node fails.
16. Atrioventricular Bundle (Bundle of His)
- Muscular structure transmitting impulses from AV node to ventricles.
17. Coronary Arteries
- Supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart.
- Branch into left and right coronary arteries.
18. Coronary Veins
- Return deoxygenated blood from the heart to the right atrium.
Quick Facts: 13 Parts of the Heart (Simplified)
If you want a simpler breakdown, here’s a list of 13 main parts of the heart to remember:
- Myocardium
- Endocardium
- Pericardium
- Right Atrium
- Right Ventricle
- Tricuspid Valve
- Pulmonary Valve
- Left Atrium
- Left Ventricle
- Mitral Valve
- Aortic Valve
- SA Node
- AV Node
FAQ
Q: How many muscles are in the heart?
A: The heart’s main muscle is the myocardium, located in all chambers, especially thick in the ventricles.
Q: What are the 13 parts of the heart?
A: The essential parts include the myocardium, endocardium, pericardium, atria, ventricles, valves, and pacemaker nodes.
Q: What is the function of the coronary arteries?
A: They supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle to maintain its pumping function.
Q: Where is the heart located?
A: Slightly left behind the sternum, protected by the ribs.

